Answer Key
Module 2: Detect a Path

Module 3: Forward, Left
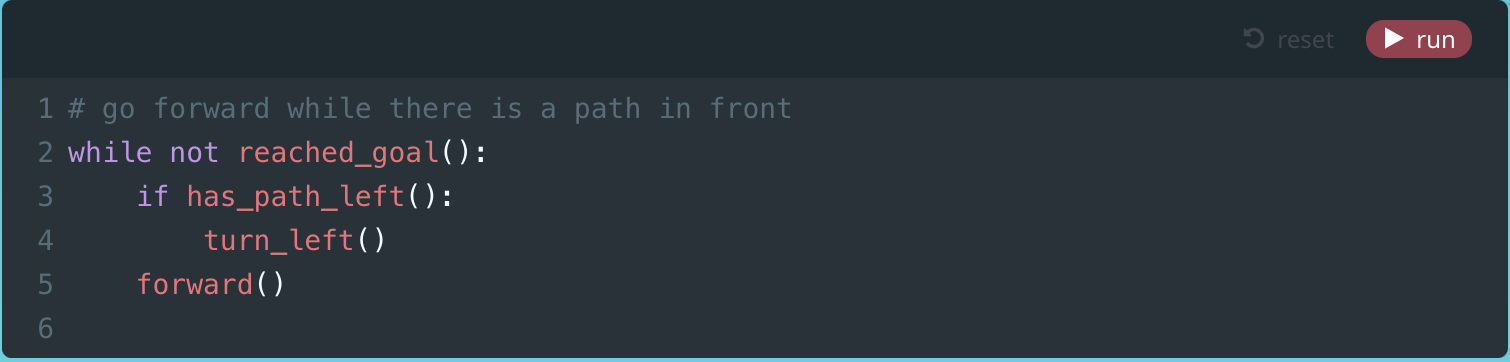
Module 4: Right, Forward
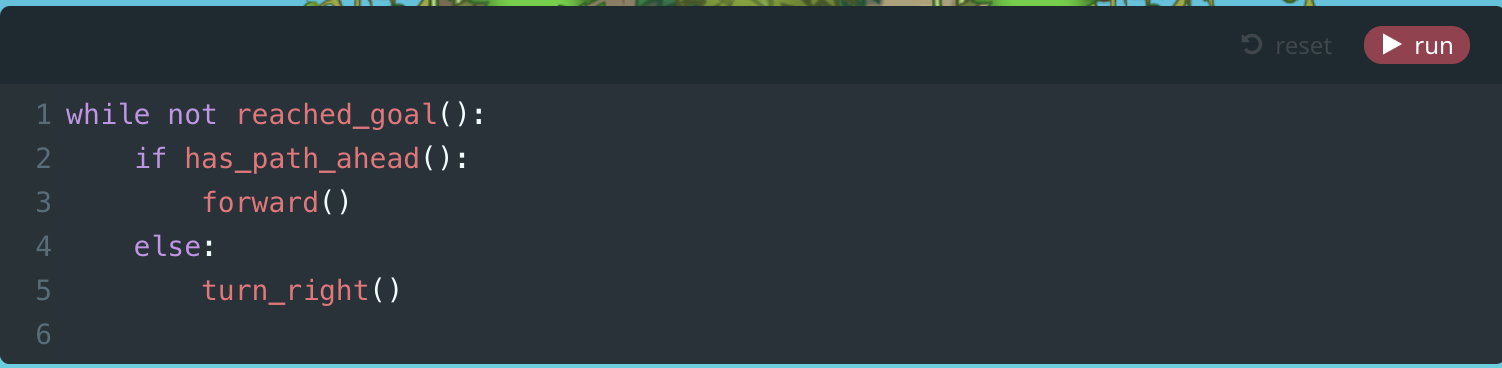
Module 7: Path Ahead?
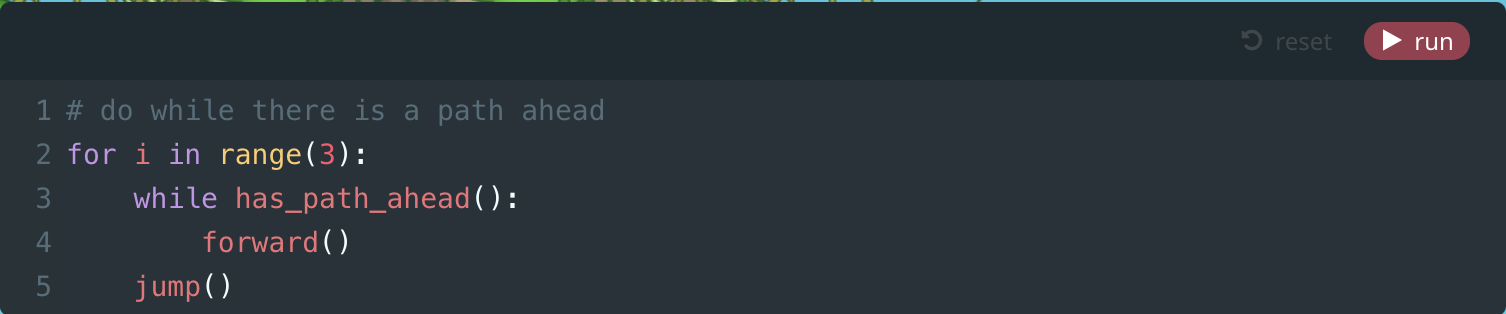
Module 8: Left Spiral
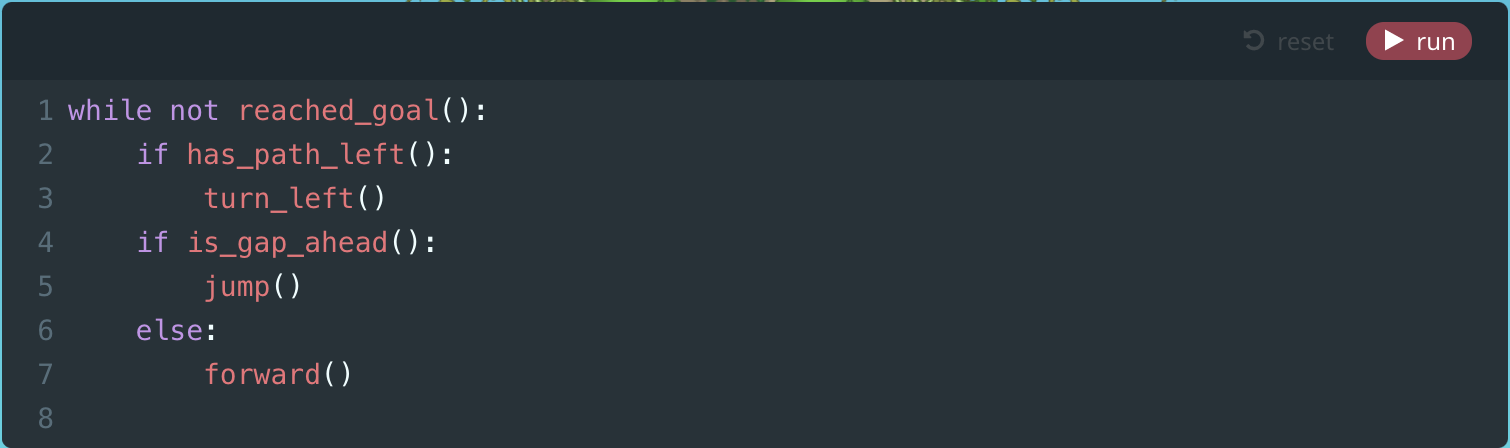
Module 9: Right Spiral
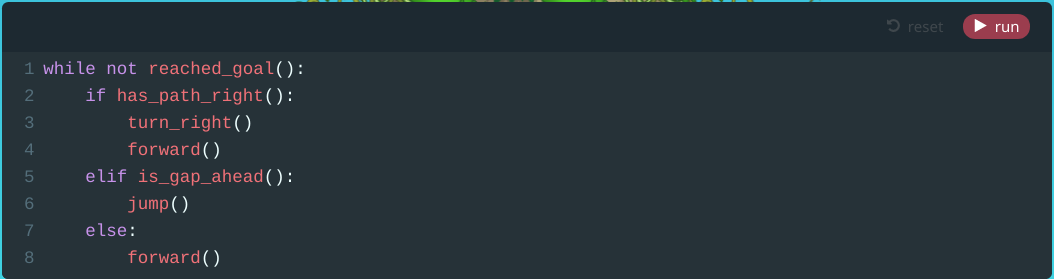
Module 10: Choose a Path
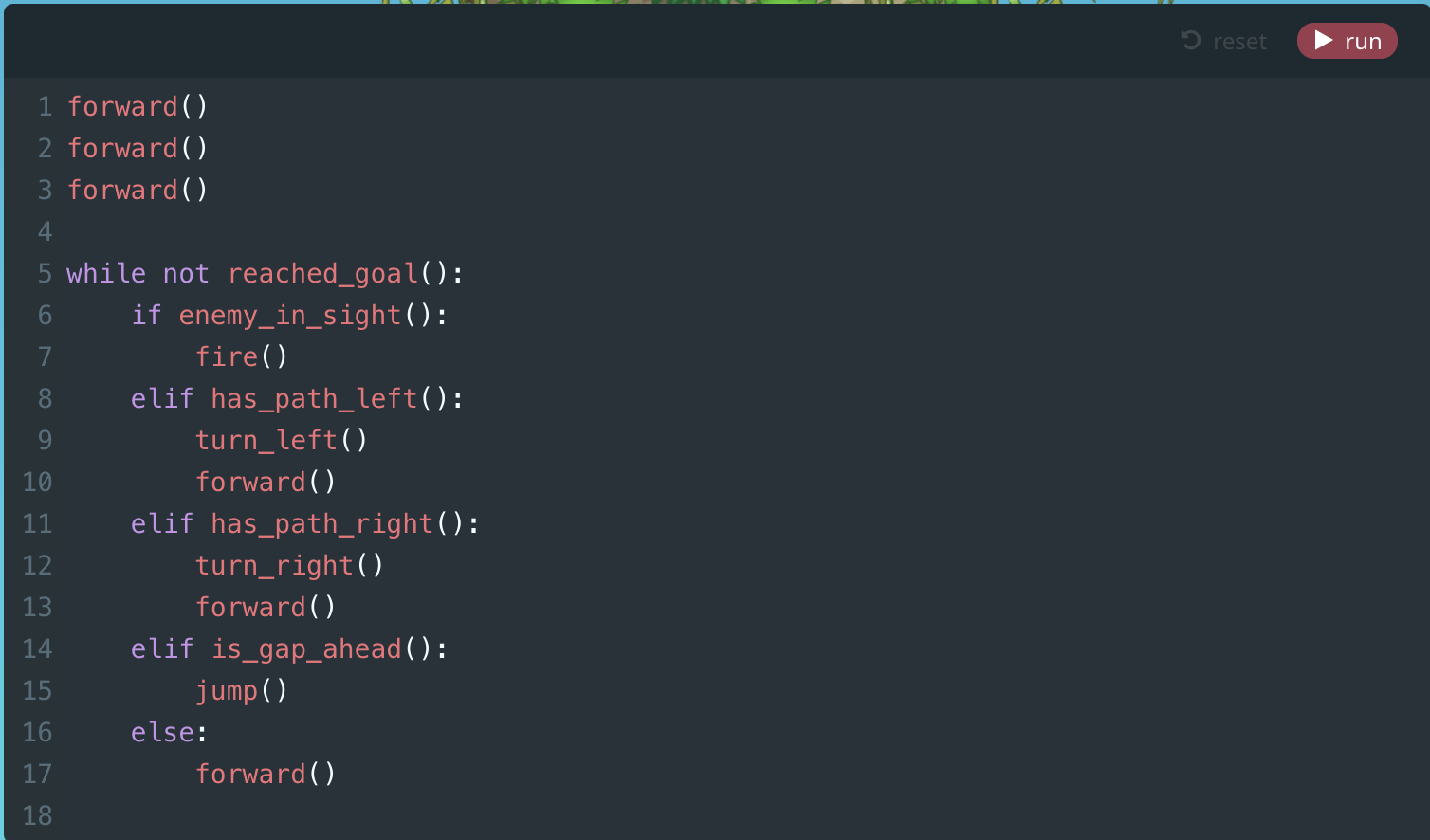
Module 12: Quiz
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
U.S. Standards
- CCSS-ELA: SL.7.1, SL.8.1, RI.9-10.3, RI.9-10.6, L.9-10.3, L.9-10.6
- CCSS-Math: HSN.Q.A.1, HSN.Q.A.2, HSN.Q.A.3, MP.1
- CSTA: 2-AP-11, 2-AP-13, 2-AP-15, 2-AP-17, 3A-AP-17, 3A-AP-19, 3B-AP-11, 3B-AP-12
- CS CA: 6-8.AP.11, 6-8.AP.13, 6-8.AP.17, 9-12.AP.12, 9-12.AP.14, 9-12.AP.16, 9-12.AP.18
- ISTE: 1.c, 1.d, 4.d, 5.c, 5.d
U.K. Standards
Key stage 3
Pupils should be taught to:- design, use and evaluate computational abstractions that model the state and behaviour of real-world problems and physical systems
- understand several key algorithms that reflect computational thinking [for example, ones for sorting and searching]; use logical reasoning to compare the utility of alternative algorithms for the same problem
- undertake creative projects that involve selecting, using, and combining multiple applications, preferably across a range of devices, to achieve challenging goals, including collecting and analysing data and meeting the needs of known users
- create, reuse, revise and repurpose digital artefacts for a given audience, with attention to trustworthiness, design and usability
- understand a range of ways to use technology safely, respectfully, responsibly and securely, including protecting their online identity and privacy; recognise inappropriate content, contact and conduct, and know how to report concerns
Key stage 4
Pupils should be taught to:- develop their capability, creativity and knowledge in computer science, digital media and information technology
- develop and apply their analytic, problem-solving, design, and computational thinking skills
- understand how changes in technology affect safety, including new ways to protect their online privacy and identity, and how to report a range of concerns
Description
In this introduction to Python for intermediate or advanced coders in upper middle or high school, students will be learn to code in Python. As they complete this advanced lesson plan, they will enjoy engaging lessons, solve challenging puzzles, and build their own games in Python. This course is ideal for students who have already completed at least one Tynker course and are comfortable with the basics of programming logic and computational thinking. This course will help them learn how to code Python and adapt to the additional challenges of text-based syntax.
Students who successfully complete this lesson plan will demonstrate a strong mastery of Python syntax, as well as the ability to creatively program games and other projects and debug their own code. Students will also be able to come up with an idea for a Python game and take it through the entire design and implementation process, creating custom versions of many of their favorite games in Python.
Topics
- Python syntax
- Sequencing
- Repetition
- Conditional logic
- Nested loops
- Automation
- Pattern recognition
- Simple motion
- Keyboard and mouse events
- Pen drawing
- Operators
- Expressions
- Variables
- Turtle graphics
- Using arrays and objects to store structured data
What Students Learn
- Learn Python syntax
- Use conditional logic, loops, and conditional loops to solve problems
- Create and use variables
- Detect and handle keyboard and mouse events
- Write and interpret Python expressions
- Use pen drawing and Turtle graphics to draw shapes and display images
- Detect win/loss conditions in a game
- Implement collision detection between images
- Use arrays, dictionaries, and objects to store structured data
Technical Requirements
* Online courses require a modern desktop computer, laptop computer, Chromebook, or Netbook with Internet access and a Chrome (29+), Firefox (30+), Safari (7+), or Edge (20+) browser. No downloads required.
Lesson
4 : Conditional Loops
Python 101
Time: 40+ minutes
Introduction
Commands Introduced
Vocabulary
Objectives
Materials
Warm-Up (5 minutes)
Activities (35 minutes)
Facilitate as students complete all Conditional Loops modules on their own:
1. What Is a "While" Loop? (Document)2. Detect a Path (Puzzle)
3. Forward, Left (Puzzle)
4. Right, Forward (Puzzle)
5. What Are "Break" and "Else"? (Document)
6. Path Ahead? (Puzzle)
7. Left Spiral (Puzzle)
8. Right Spiral (Puzzle)
9. Choose a Path (Puzzle)
10. Review (Document)
11. Quiz (Multiple Choice)
