Answer Key
Module 9: Quiz
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
U.S. Standards
- CCSS-Math: 3.NBT.A.2, MP.1
- CCSS-ELA: RF.3.4.A, RF.4.4.A
- CSTA: 1B-AP-11, 1B-AP-12, 1B-AP-15
- CS CA: 3-5.AP.13, 3-5.AP.14, 3-5.AP.17
- ISTE: 1.c, 1.d, 4.d, 5.c, 5.d, 7.c
U.K. Standards
Key stage 2
Pupils should be taught to:- design, write and debug programs that accomplish specific goals, including controlling or simulating physical systems; solve problems by decomposing them into smaller parts
- use sequence, selection, and repetition in programs; work with variables and various forms of input and output
- use logical reasoning to explain how some simple algorithms work and to detect and correct errors in algorithms and programs
- understand computer networks, including the internet; how they can provide multiple services, such as the World Wide Web, and the opportunities they offer for communication and collaboration
- use search technologies effectively, appreciate how results are selected and ranked, and be discerning in evaluating digital content
- select, use and combine a variety of software (including internet services) on a range of digital devices to design and create a range of programs, systems and content that accomplish given goals, including collecting, analysing, evaluating and presenting data and information
- use technology safely, respectfully and responsibly; recognise acceptable/unacceptable behaviour; identify a range of ways to report concerns about content and contact
Description
Advance your class to intermediate level programming concepts using a wider set of visual blocks. In Snowball Siege, students learn about layering, Actor visibiliy, motion, and collisions. Then, in Star Runner, they use line drawing commands and program math art. They build several mini-games while understanding how to create more complex programs. After completing this lesson plan, students will be able to build a wide variety of school projects and their own comprehensive games.
Topics
- Animation sequences
- Motion
- Game design basics
- Built-in animation commands
- Advanced keyboard and mouse control
- Sending and receiving messages
- Actor layering
- Advanced events
- Math operators
- Functions
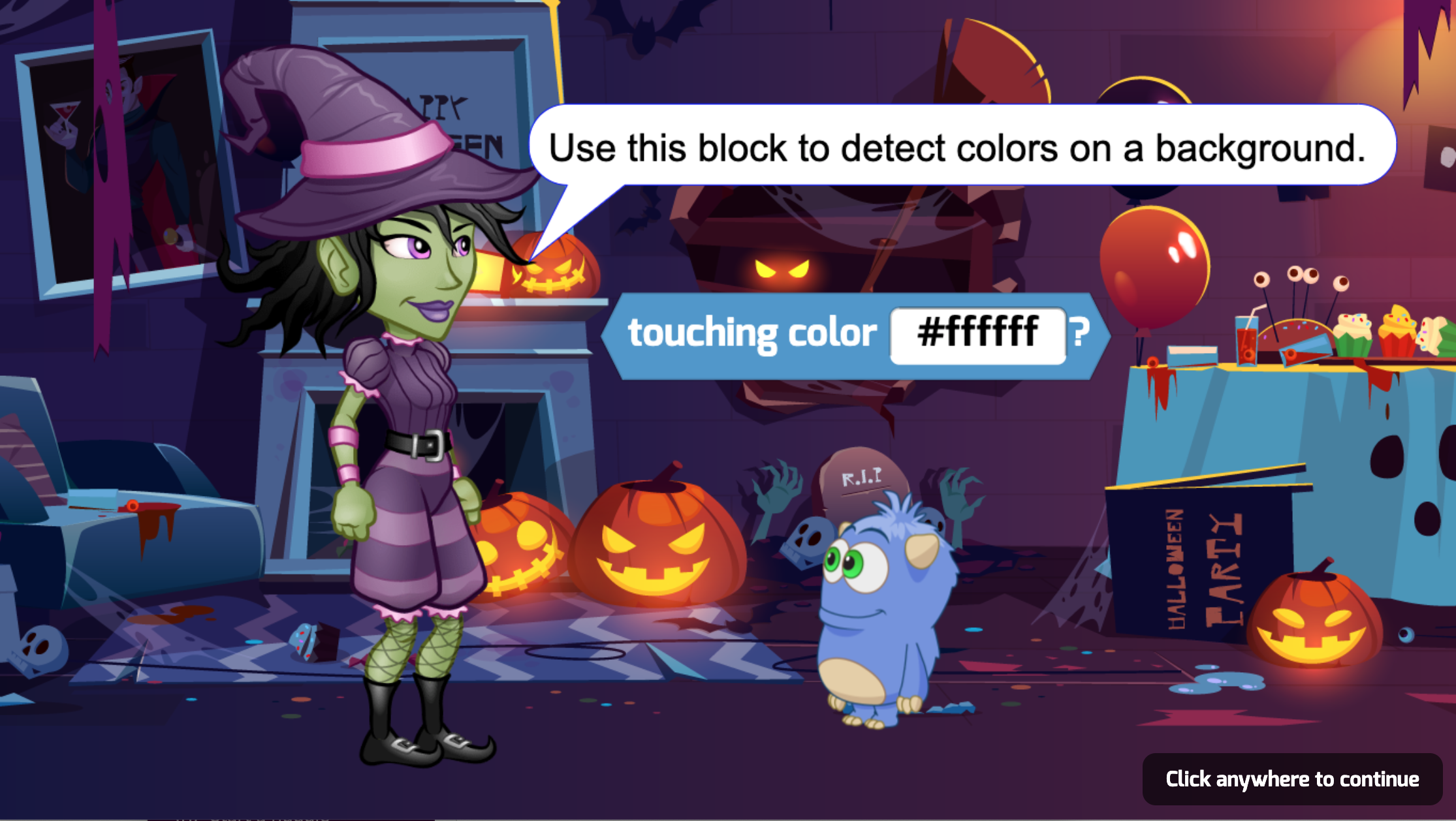

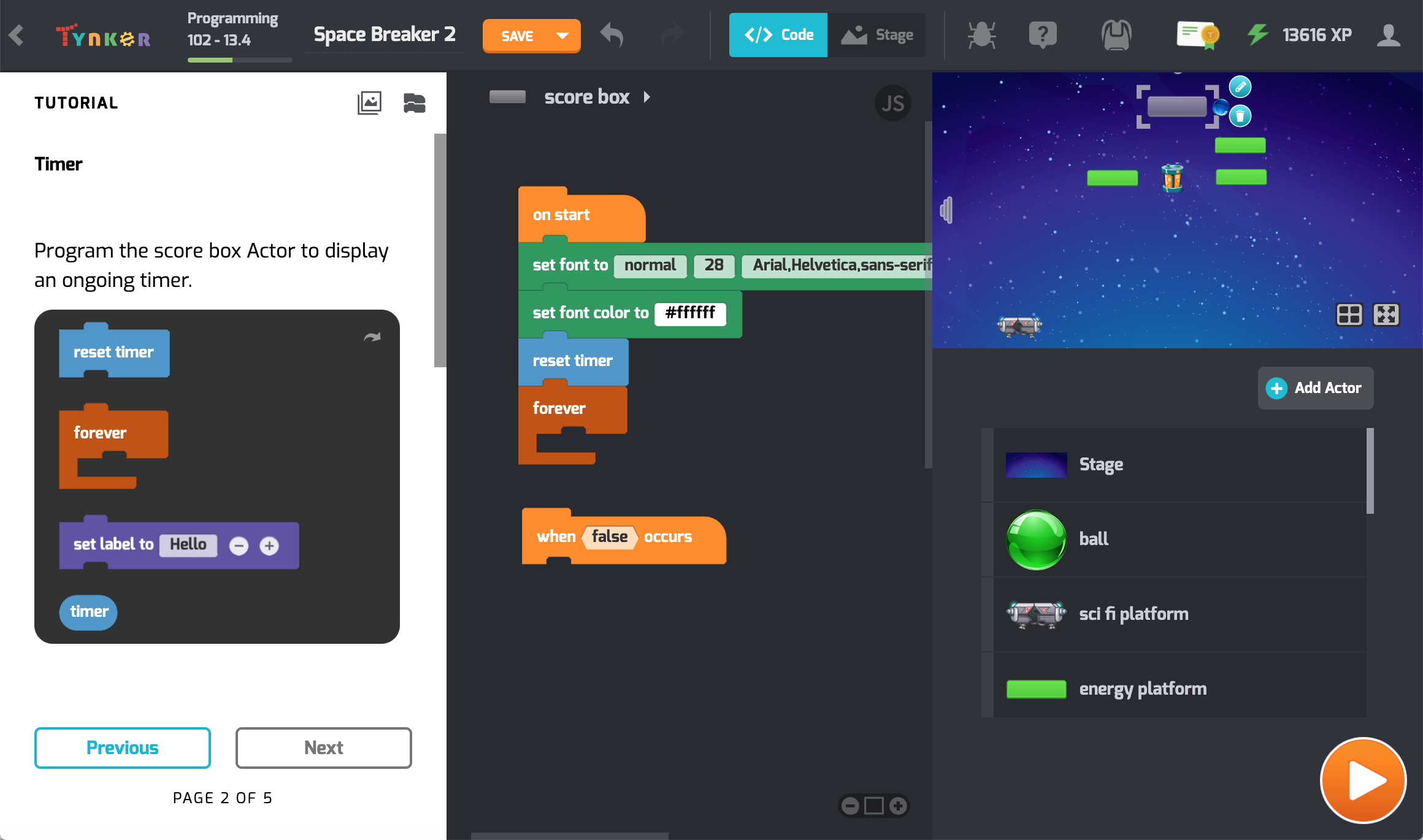
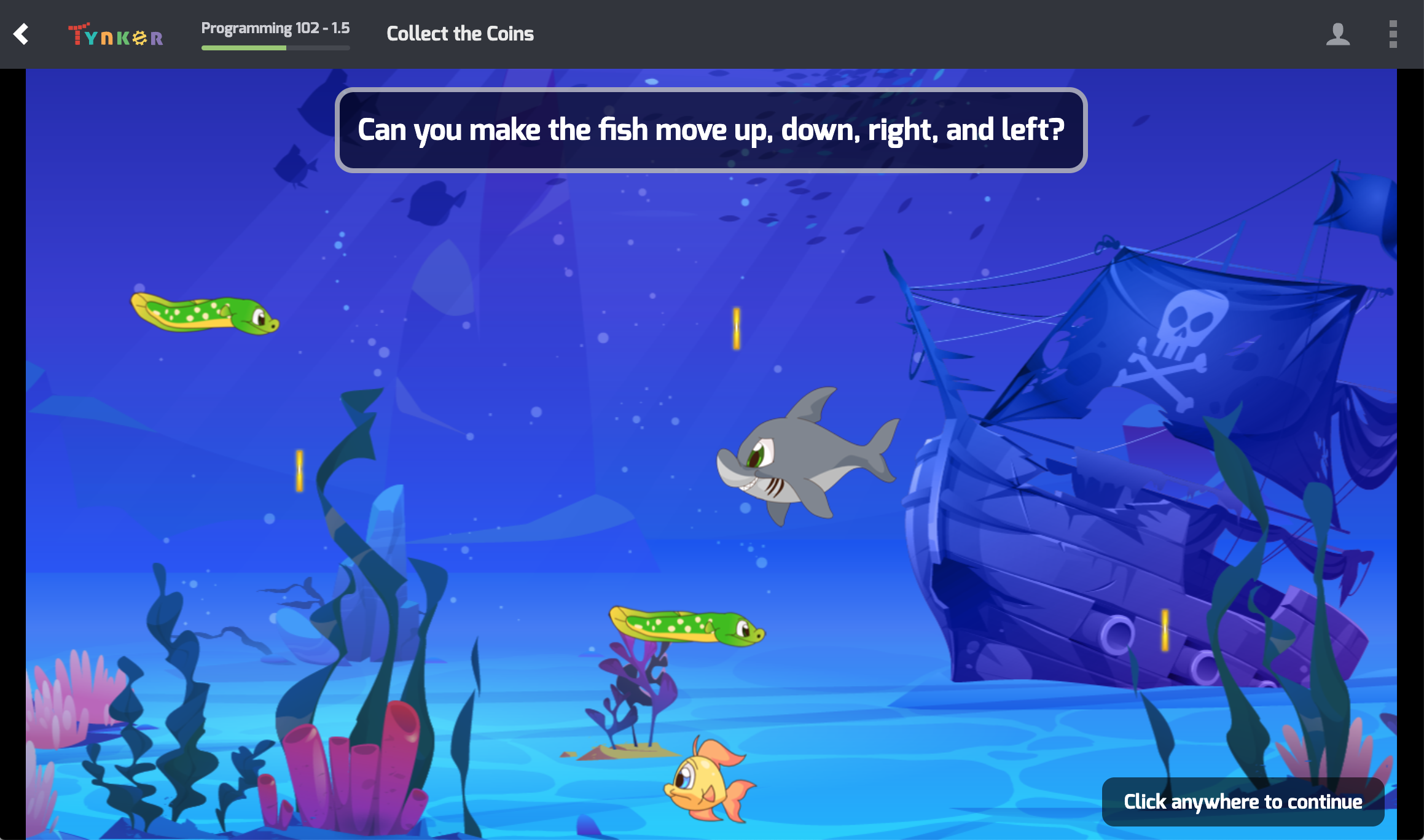

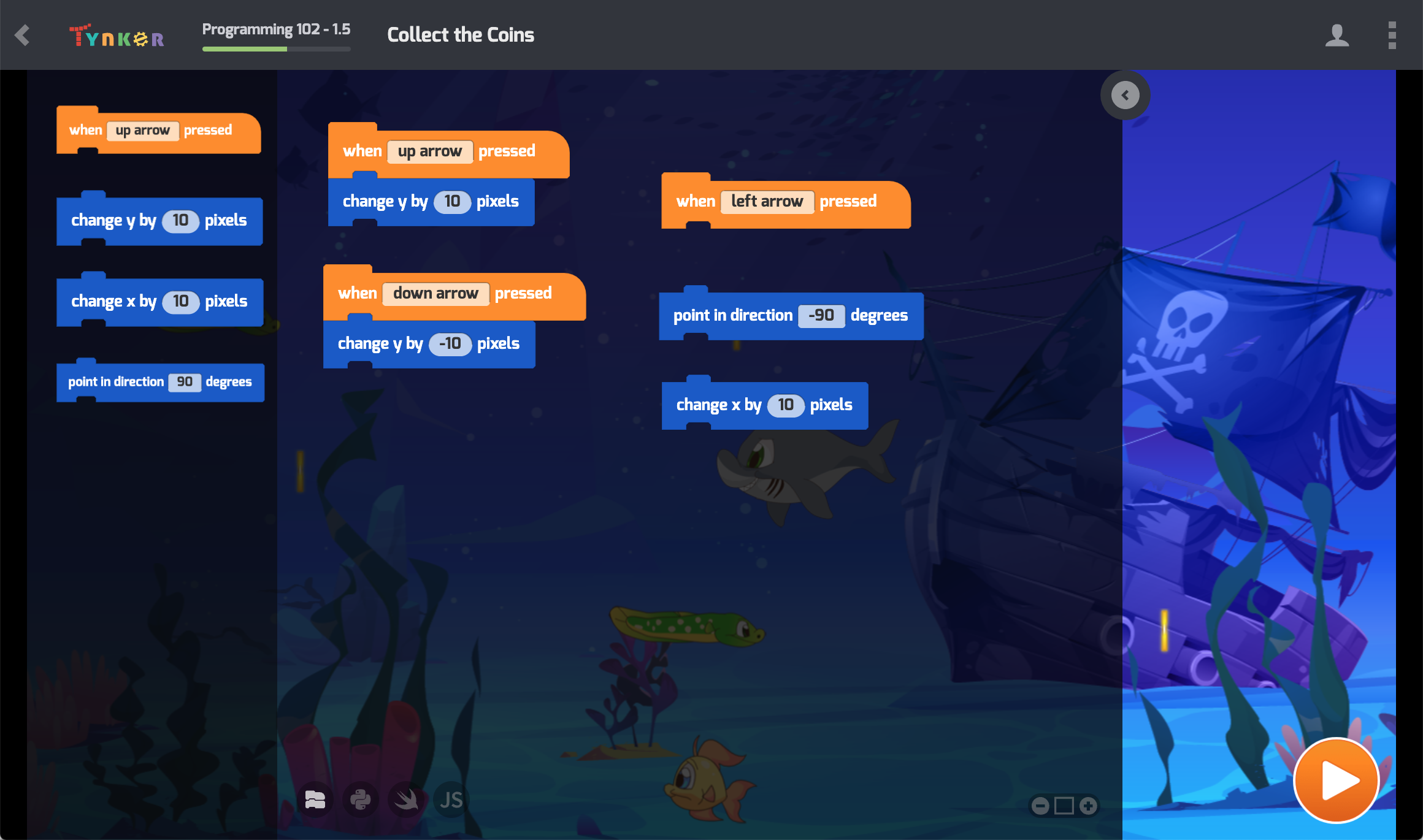

What Students Learn
- Gain confidence in building a variety of programs
- Apply programming concepts to build your own games
- Design characters with multiple animation sequences
- Write interactive stories with multiple scenes
- Make an image editor using drawing primitives
- Define more advanced keyboard and mouse interaction
- Program special effects and explosions
- Troubleshoot and debug programs
Technical Requirements
* Online courses require a modern desktop computer, laptop computer, Chromebook, or Netbook with Internet access and a Chrome (29+), Firefox (30+), Safari (7+), or Edge (20+) browser. No downloads required.
* Tablet courses require an iPad (iOS 10+) with Tynker or Tynker Junior app installed and Internet access
Lesson
12 : Star Runner
Programming 102
Time: 60+ minutes
Introduction
Tynker Blocks Introduced
Vocabulary
Objectives
Materials
Warm-Up (15 minutes)
Activities (45 minutes)
Facilitate as students complete all Star Runner modules on their own:
1. Introduction (Introduction)2. Concepts (Concepts)
3. Shoot the Enemy Example (Example)
4. Shoot Lasers (DIY)
5. Spawn the Stars (DIY)
6. Shoot the Enemy Ship (DIY)
7. Star Runner Game (Example)
8. Star Runner Game (DIY)
9. Quiz (Multiple-Choice)




