U.S. Standards
- CCSS-Math: MP.1, MP.2, MP.4
- CCSS-ELA: RF.3.4, RF.4.4, RF.5.4 RF.3.4.A, RF.4.4.A, RF.5.4.A
- CSTA: 1B-CS-01, 1B-CS-02, 1B-AP-10, 1B-AP-11, 1B-AP-12, 1B-AP-15
- CS CA: 3-5.AP.10, 3-5.AP.12, 3-5.AP.13, 3-5.AP.14, 3-5.AP.17
- ISTE: 1.c, 1.d, 4.d, 5.c, 5.d, 6.b
U.K. Standards
Key stage 2
Pupils should be taught to:- design, write and debug programs that accomplish specific goals, including controlling or simulating physical systems; solve problems by decomposing them into smaller parts
- use logical reasoning to explain how some simple algorithms work and to detect and correct errors in algorithms and programs
- understand computer networks, including the internet; how they can provide multiple services, such as the World Wide Web, and the opportunities they offer for communication and collaboration
- use technology safely, respectfully and responsibly; recognise acceptable/unacceptable behaviour; identify a range of ways to report concerns about content and contact
Description
Introduce your class to physical computing with micro:bit online and Tynker Blocks. The micro:bit is a tiny, microcomputer with programmable LEDs, light, and temperature sensors, physical connection pins, motion sensors, and wireless communication via radio and Bluetooth. Hands-on learning with Tynker’s curriculum engages students as they see their abstract programs come to life on a tangible physical device.
Using a combination of interactive micro:bit lessons, concept explanations, videos, puzzles, quizzes, and DIY projects, this course teaches students to write block coding programs and then deploy the code to the micro:bit wirelessly. Students can use code to program physical buttons, display messages on the micro:bit, animate the LEDs, simulate dice and coin flips, and detect gestures and shakes.
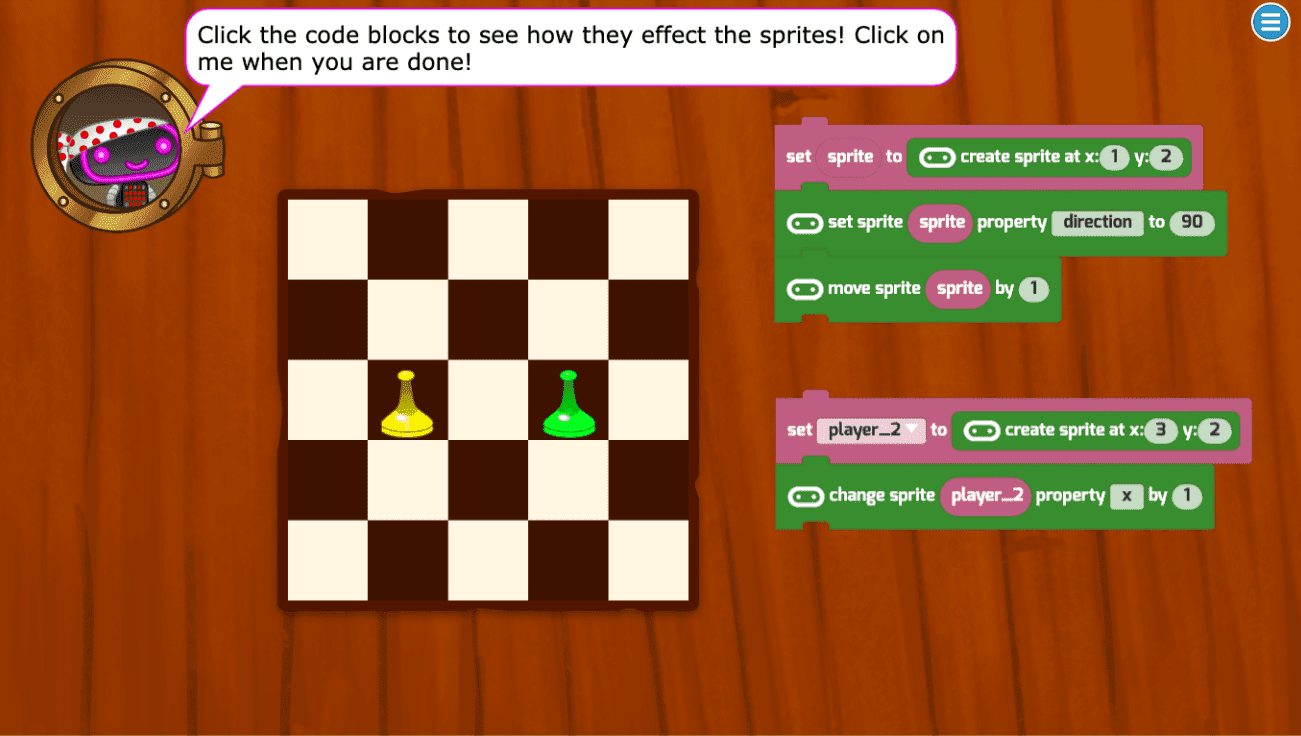
The micro:bit coding lesson plans in this course build and reinforce engineering, math, and science skills, while applying programming concepts such as repetition, events, conditional logic, variables, and functions with a physical computing device.
Each lesson is designed for a class period of 45-60 minutes. All student work is automatically tracked and assessed, and you'll be able to monitor individual progress and mastery charts for your students.
This course is recommended for students who are just starting to get familiar with block programming. More advanced students who are familiar with Python may enroll in MicroPython 101 where they use MicroPython, a Python-like text-based programming language to program micro:bit.
This micro:bit code course is supported online as well as on an iPad through the Tynker app.
Recommended Accessories: This course requires micro:bit devices (not included). You may purchase these separately at a variety of resellers.
- micro:bit, USB cable, Battery pack, 2xAAA batteries (for each student or group)
Topics
- micro:bit command library
- Variables
- Deploying code to the micro:bit
- Types of loops
- Reading sensor values
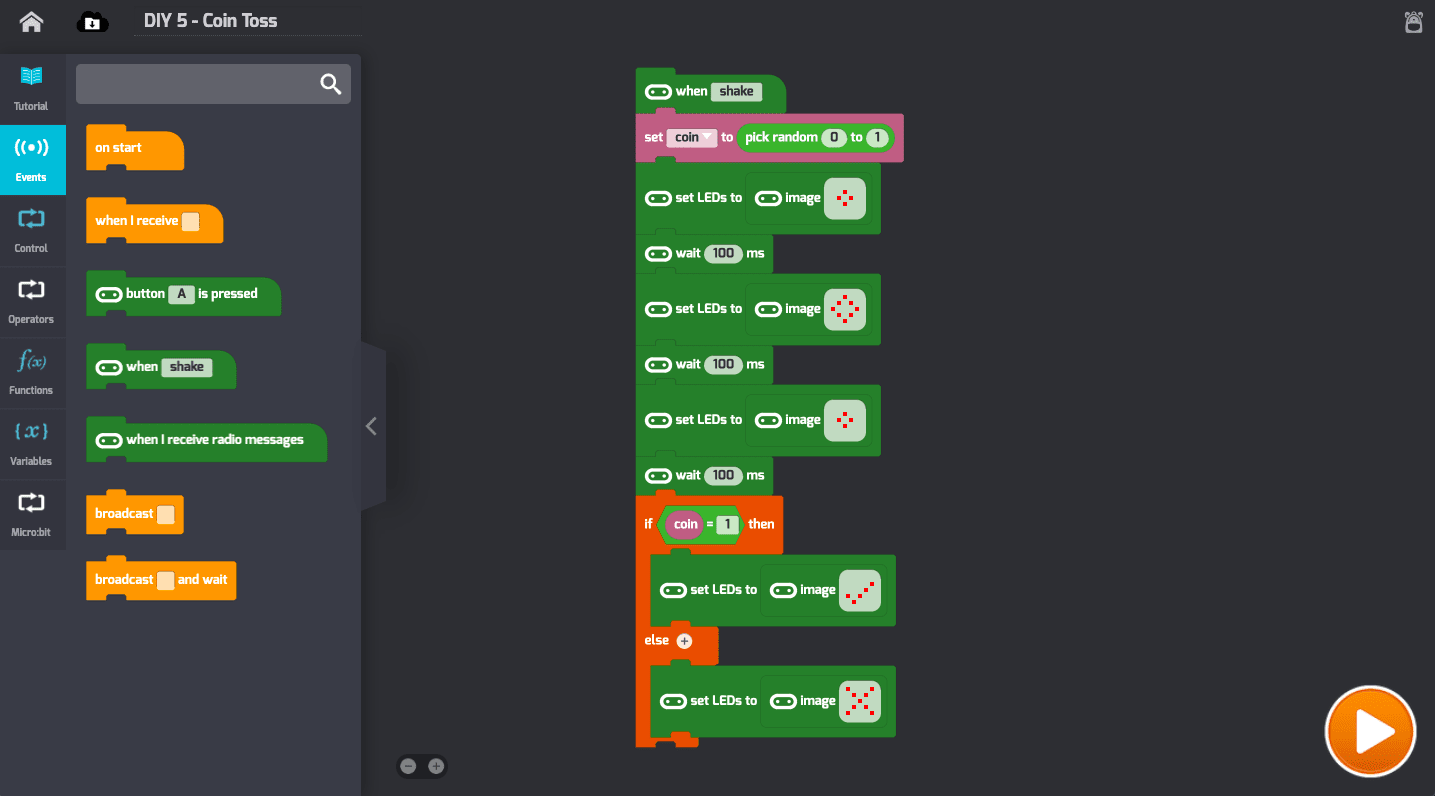
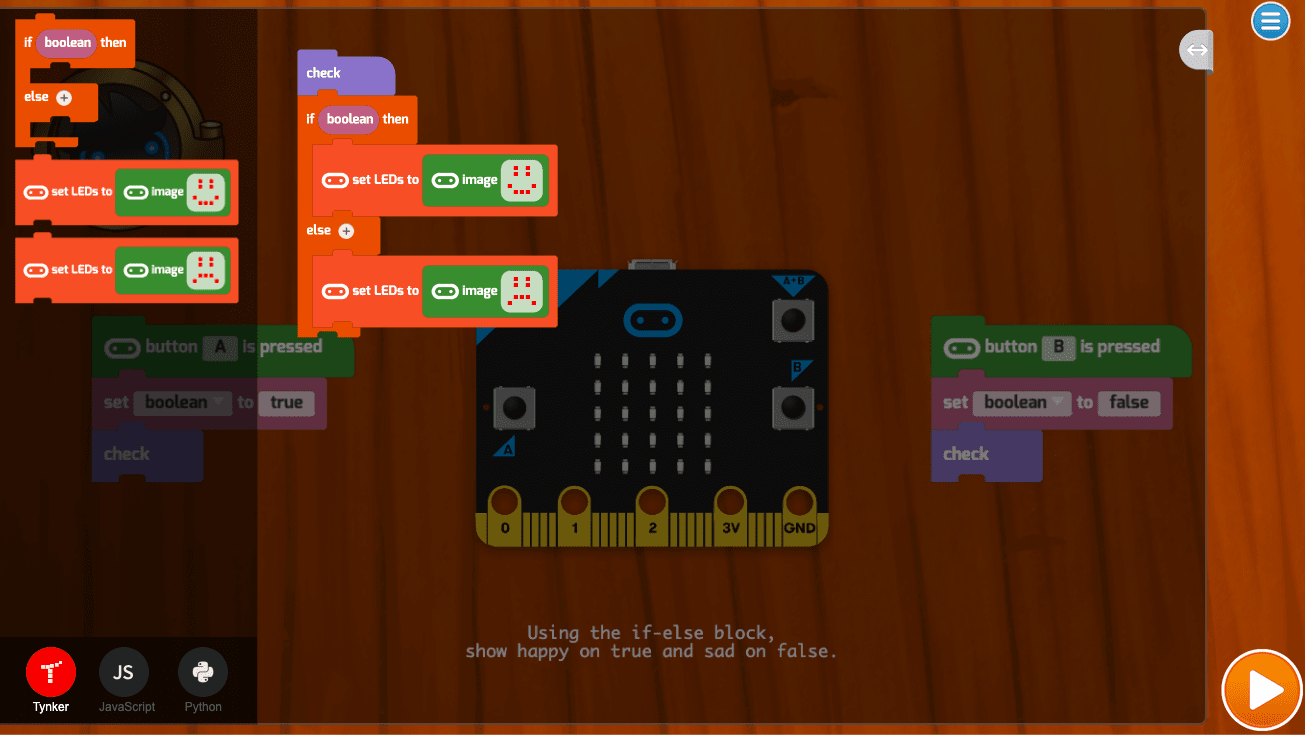
- Conditional logic
- Programming the LED grid
- Lists and arrays


What Students Learn
- Program micro:bit button-click events
- Display a scrolling message on the micro:bit
- Create animated LED displays using loops
- Simulate a coin toss using conditional logic
- Create a virtual die using random numbers
- Detect gestures using the motion sensor
- Learn to use math operators and expressions
Technical Requirements
* Online courses require a modern desktop computer, laptop computer, Chromebook, or Netbook with Internet access and a Chrome (29+), Firefox (30+), Safari (7+), or Edge (20+) browser. No downloads required.
* Tablet courses require an iPad (iOS 10+) with Tynker or Tynker Junior app installed and Internet access
Lesson
10 : Pins
Intro to micro:bit
Time: 45+ minutes
Introduction
Tynker Blocks Introduced
Vocabulary
Objectives
Materials
Warm-Up (5 minutes)
Activities (45 minutes)
Facilitate as students complete all Pins modules on their own:
1. Introduction (Introduction)2. Digital Pins (Introduction)
3. Analog Pins (Introduction)
4. Power and Ground (Introduction)
5. Chapter Puzzle (Puzzle)
6. DIY (DIY)
7. Quiz (Multiple-choice)
